Accuracy Mapping: The Transformative Power of 3D Laser Scanning in Connecticut
Benefits of 3D laser scanning in Connecticut .In an age where technological advancements improve sectors at an unprecedented price, one field experiencing profound improvement is mapping and evaluating. Among one of the most innovative advancements is 3D laser scanning, a modern technology that's reinventing precision mapping in Connecticut. This state, with its varied topography and dense metropolitan areas, provides special challenges and possibilities for mapping and evaluating. 3D laser scanning is addressing these obstacles, providing exceptional accuracy and efficiency.
Understanding 3D Laser Scanning
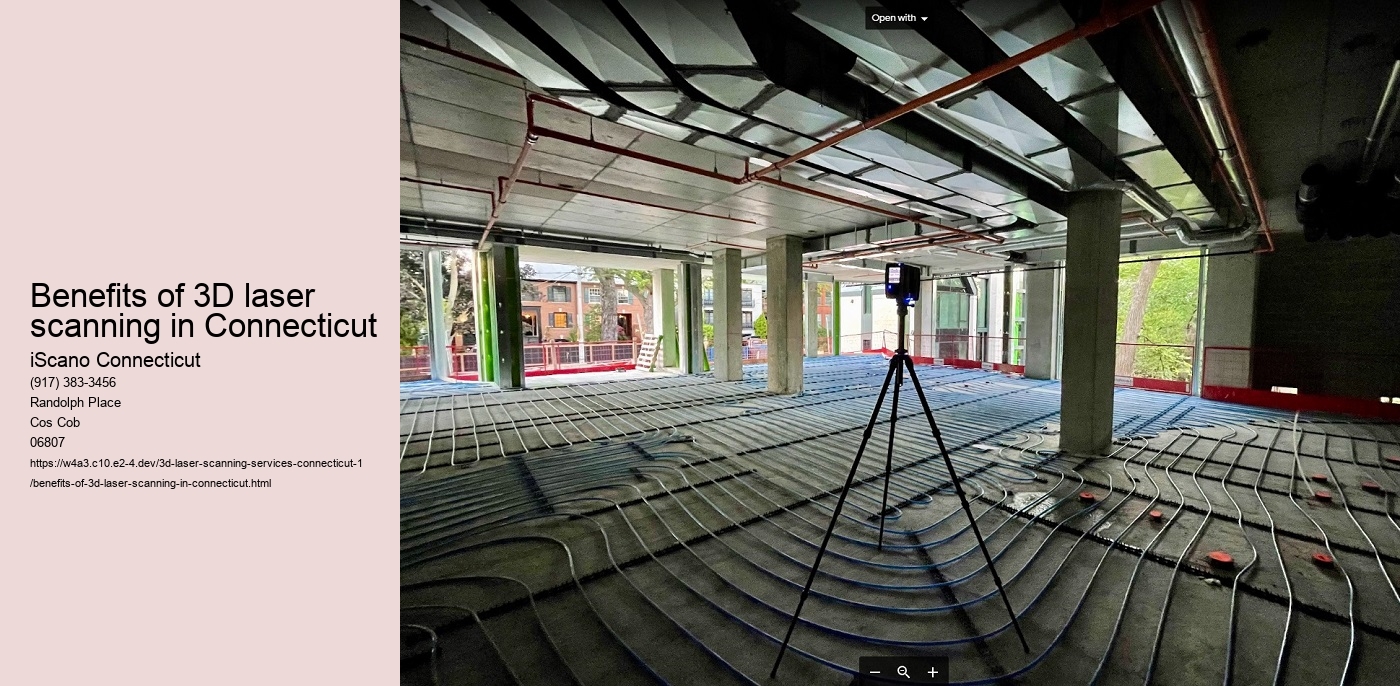
3D laser scanning, additionally called LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), is a remote sensing technique that makes use of light in the type of a pulsed laser to gauge variable ranges to the Planet. These light pulses, incorporated with various other data taped by the airborne system, create specific, three-dimensional info concerning the form and surface area characteristics of the landscape. The outcome is a very detailed and precise digital depiction of the checked atmosphere.
The technology works by emitting laser light beams in the direction of a target surface area. When these beams hit the surface area, they are mirrored back to the scanner, which gauges the moment it takes for the light to return. This time-of-flight data is after that used to determine the range between the scanner and the target. By rapidly duplicating this procedure numerous times per second, the scanner develops a comprehensive 3D point cloud—-- a dense collection of points representing the scanned location.
Applications in Connecticut
Urban Preparation and Development
Connecticut’s city facilities, such as Hartford, New Sanctuary, and Bridgeport, benefit substantially from 3D laser scanning. Urban planners and programmers utilize this innovation to produce thorough models of existing structures and landscapes. These designs help with even more precise preparation and layout, allowing for much better assimilation of brand-new advancements with existing metropolitan textile.
As an example, 3D laser scanning can record the elaborate details of historic buildings, making sure that new developments value the building heritage of the area. In addition, it helps in the preparation of framework jobs like roadways, bridges, and public transportation systems by supplying accurate topographical information. This level of detail aids coordinators anticipate possible issues and design remedies that decrease disturbances throughout building.
Ecological Conservation
Connecticut is understood for its abundant all-natural landscapes, including woodlands, rivers, and coastal areas. 3D laser scanning plays an essential duty in environmental conservation initiatives by offering detailed and exact data on these natural attributes. Conservationists use this data to keep an eye on modifications in the environment, such as erosion, deforestation, and habitat loss.
For instance, coastal erosion is a substantial issue in Connecticut. By utilizing 3D laser scanning, scientists can develop topographic maps of the coast and screen changes in time. This information assists in developing strategies to alleviate erosion and protect valuable coastal environments. Likewise, in forestry management, LiDAR technology enables the mapping of tree cover frameworks, assisting in the evaluation of woodland wellness and biodiversity.
Historic Conservation
Connecticut is home to lots of historical sites and spots. Maintaining these treasures for future generations is a concern, and 3D laser scanning is an important tool in this effort. The technology permits the development of precise digital models of historic structures, capturing every detail with high precision.
These digital models serve multiple functions. They can be made use of for documents and archival, guaranteeing that precise records of the frameworks exist also if the physical buildings are harmed or weaken over time. Additionally, the versions can be used in restoration jobs, giving designers and contractors with in-depth plans that assist in preserving the credibility of the original designs.
Facilities Upkeep
Preserving infrastructure is a consistent challenge for any kind of state, and Connecticut is no exemption. Roads, bridges, passages, and various other vital framework call for normal inspections and maintenance to make certain safety and security and functionality. 3D laser scanning boosts this process by giving comprehensive and exact information on the problem of these frameworks.
As an example, bridges go through damage because of continuous usage and environmental factors. Traditional evaluation approaches can be taxing and may not constantly discover refined signs of wear and tear. 3D laser scanning, however, can swiftly catch comprehensive pictures of a bridge's surface area, identifying cracks, contortions, and various other indicators of damages that might be missed by the nude eye. This enables more proactive repair and maintenance, potentially expanding the life-span of the infrastructure and enhancing safety and security.
Advantages of 3D Laser Scanning
The fostering of 3D laser scanning in Connecticut brings various advantages, making it a preferred selection for various applications.
High Precision and Detail
Among the most considerable advantages of 3D laser scanning is its capability to catch highly exact and in-depth information. Typical surveying techniques, while efficient, frequently entail a degree of estimation and can be time-consuming. In contrast, 3D laser scanning supplies specific dimensions with millimeter accuracy, considerably reducing the margin of error.
Speed and Efficiency
3D laser scanning is remarkably quick compared to conventional approaches. A single scan can capture millions of information factors in an issue of minutes. This speed converts to raised effectiveness in data collection, permitting jobs to move on faster. For instance, evaluating a large building site that would certainly take days using conventional methods can be completed in a few hours with 3D laser scanning.
Safety and security
Safety is a paramount issue in many evaluating and mapping tasks, particularly those entailing unsafe or hard-to-reach locations. 3D laser scanning enhances security by enabling data collection from a range. Surveyors can run the scanners remotely, decreasing the need to literally access hazardous places.
Comprehensive Data Collection
The point cloud data created by 3D laser scanning offers a comprehensive and comprehensive view of the checked setting. This data can be made use of for various analyses, including topographical mapping, volumetric computations, and structural assessments. The versatility of the information allows it to be made use of across various stages of a project, from preliminary preparation to final evaluation.
Combination with Other Technologies
3D laser scanning information can be conveniently integrated with various other modern technologies, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Building Information Modeling (BIM), and augmented reality. This integration boosts the value of the information by allowing it to be used in a vast array of applications. As an example, integrating 3D laser scanning information with BIM permits more precise and in-depth structure styles, enhancing building quality and effectiveness.
Difficulties and Future Prospects
While 3D laser scanning offers many benefits, it is not without its obstacles. The first price of the equipment and software application can be high, which may be an obstacle for smaller sized companies or jobs with minimal budgets. In addition, the modern technology needs specialized training to run and interpret the data correctly.
Data management is an additional difficulty. The factor clouds produced by 3D laser scanning can be big and complex, calling for considerable storage space and handling power. Successfully managing and examining this data can be demanding, demanding durable IT facilities and expertise.
Despite these challenges, the future of 3D laser scanning in Connecticut looks encouraging. As technology breakthroughs, costs are expected to decrease, making it more easily accessible to a more comprehensive series of users. Improvements in data processing and monitoring will likewise make it much easier to handle huge datasets, further enhancing the energy of 3D laser scanning.
In addition, continuous growths in related fields, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, are likely to match 3D laser scanning. These technologies can help automate data analysis, identify patterns, and make predictive evaluations, adding an additional layer of value to the data gathered with 3D laser scanning.
Final thought
3D laser scanning is transforming accuracy mapping and surveying in Connecticut, offering unprecedented precision, performance, and security. Its applications span metropolitan planning, environmental conservation, historical preservation, and framework maintenance, among others. Regardless of the obstacles, the technology's benefits make it an effective tool for a wide range of tasks.
As Connecticut continues to grow and develop, 3D laser scanning will play an important function in guaranteeing that this growth is handled in a sustainable and effective fashion. The comprehensive and exact information offered by this innovation will aid coordinators, programmers, and guardians make educated choices, preserving the state's all-natural and social heritage while promoting progress and advancement.